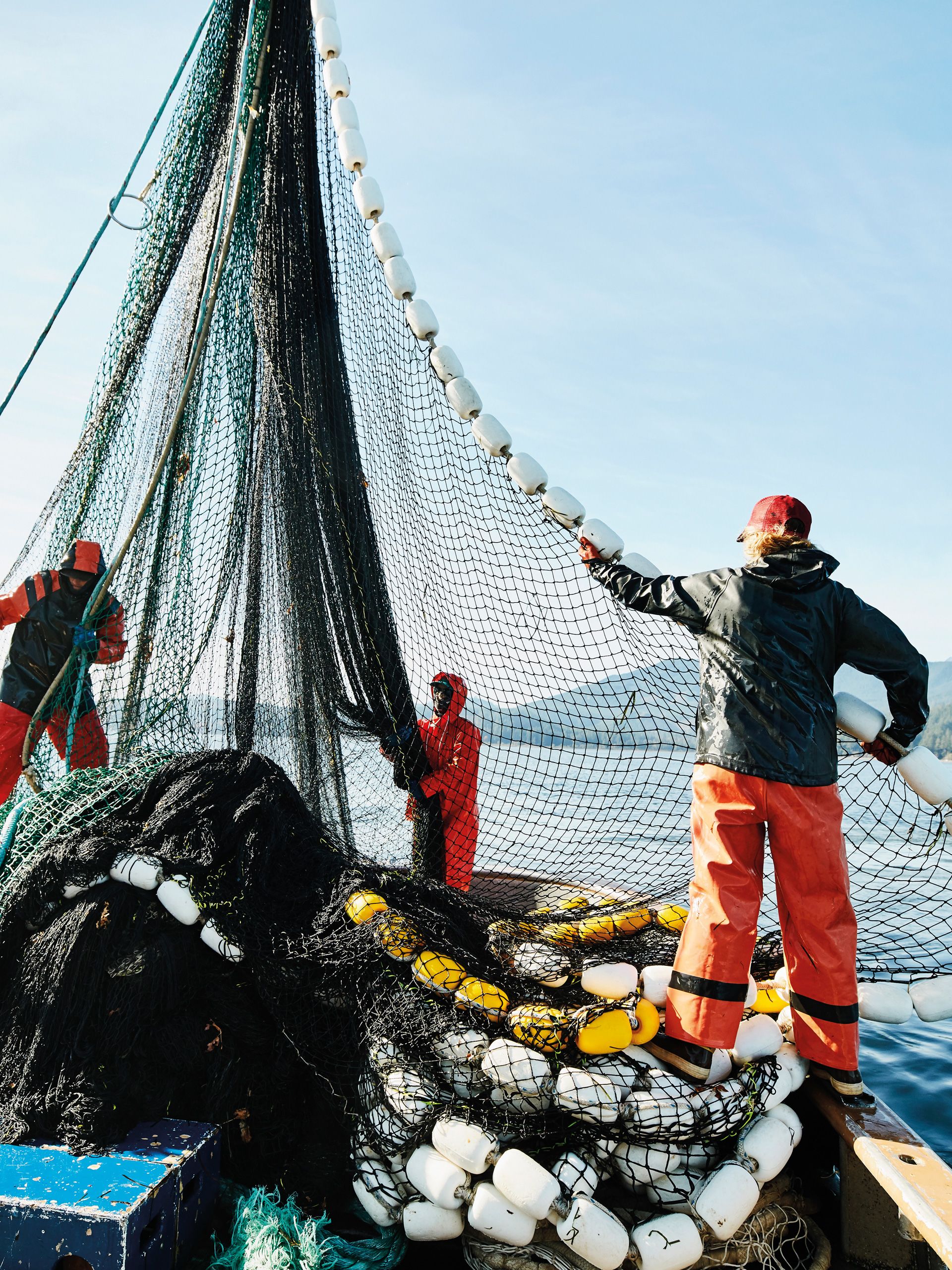
Celebrating 80 Years

Celebrating
80 Years of
improving human
and planet health
Since 1944, NSF has worked to improve human and planet health by developing and implementing public and environmental health standards.

Walking in a tea plantation in Sao Miguel, Azores

Chair’s Foreword
As the Chair of the Board, I am profoundly honored to have played a role in supporting the mission of NSF over the past three decades. In that time, I have watched this remarkable organization evolve and grow, adapting to a changing world while steadfastly upholding its commitment to scientific rigor and the protection of human and planet health. In the pages that follow, I am thrilled to share with you a glimpse into NSF’s inspiring journey, from its establishment in 1944 to its exciting trajectory for the future.
The world has undergone profound transformations since I first became associated with NSF. Technology has reshaped our lives, and global challenges have become more complex. Yet, throughout these changes, NSF has remained unwavering in its dedication to its core mission and scientific integrity. Our ability to innovate and expand our reach into new areas, always with a focus on safeguarding human and planet health, has been a driving force behind our enduring relevance.
As we embark on this new chapter of NSF’s history, we have welcomed new leaders and directors who bring fresh perspectives and ideas. This infusion of talent and energy has invigorated our commitment to excellence. NSF is the extraordinary company it is today because of the team of people who work for it.
As we celebrate our 80th anniversary, I am not only looking back at our accomplishments but also eagerly anticipating the impact NSF will continue to have in the years to come. The world may change, but our mission remains constant: to improve human and planet health. I am excited about the boundless possibilities that lie ahead and the contributions that NSF will make to champion a safer, healthier, and more sustainable future.
Thomas Glasgow Jr.
Chair of the Board, NSF

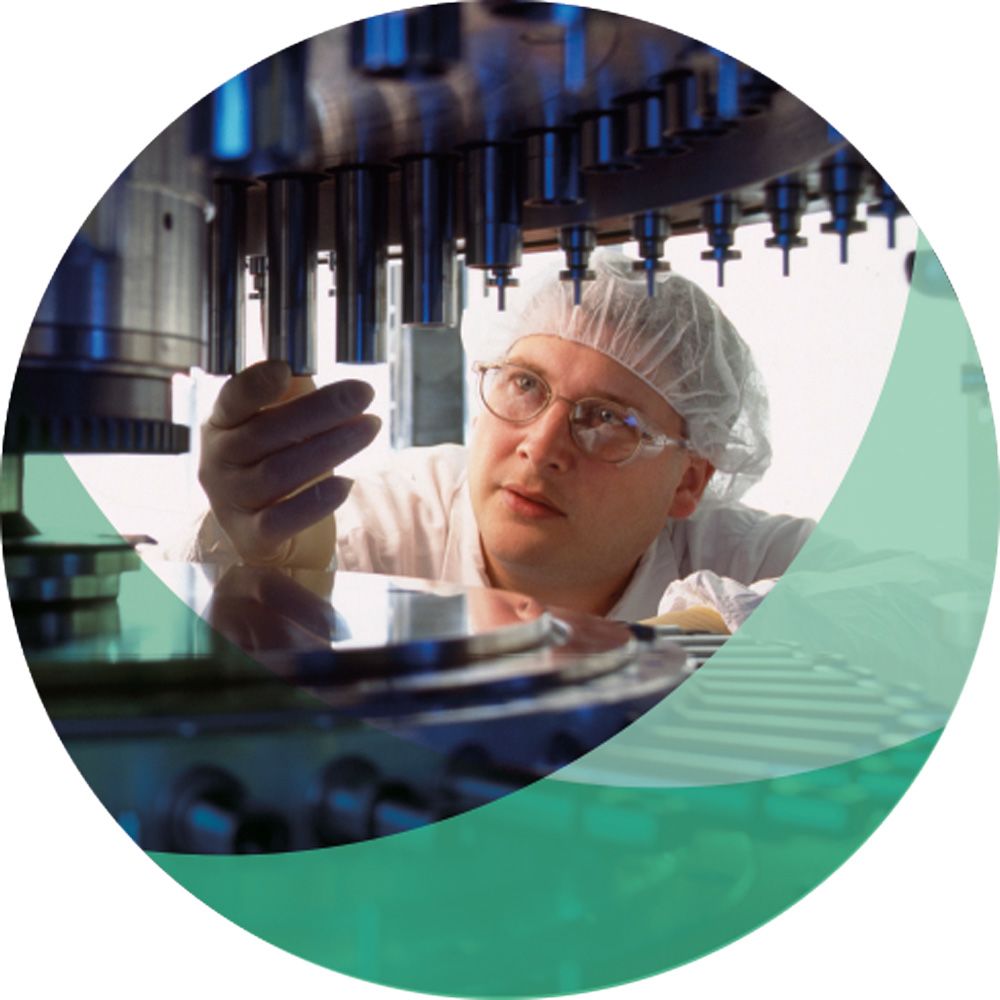
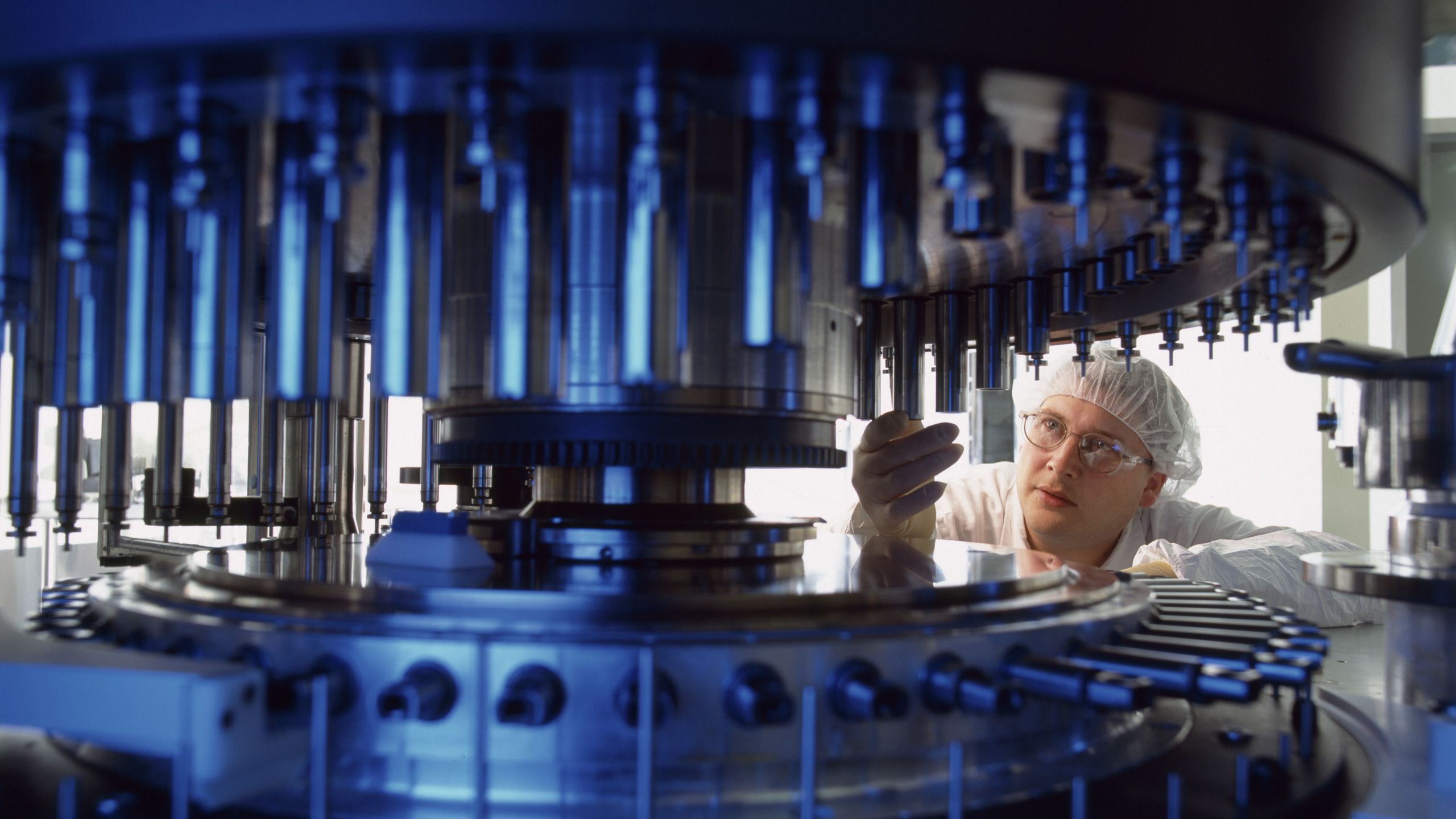
Pioneering Public Safety since 1944
1
For 80 years, NSF has been building its reputation as a leading force in public health.


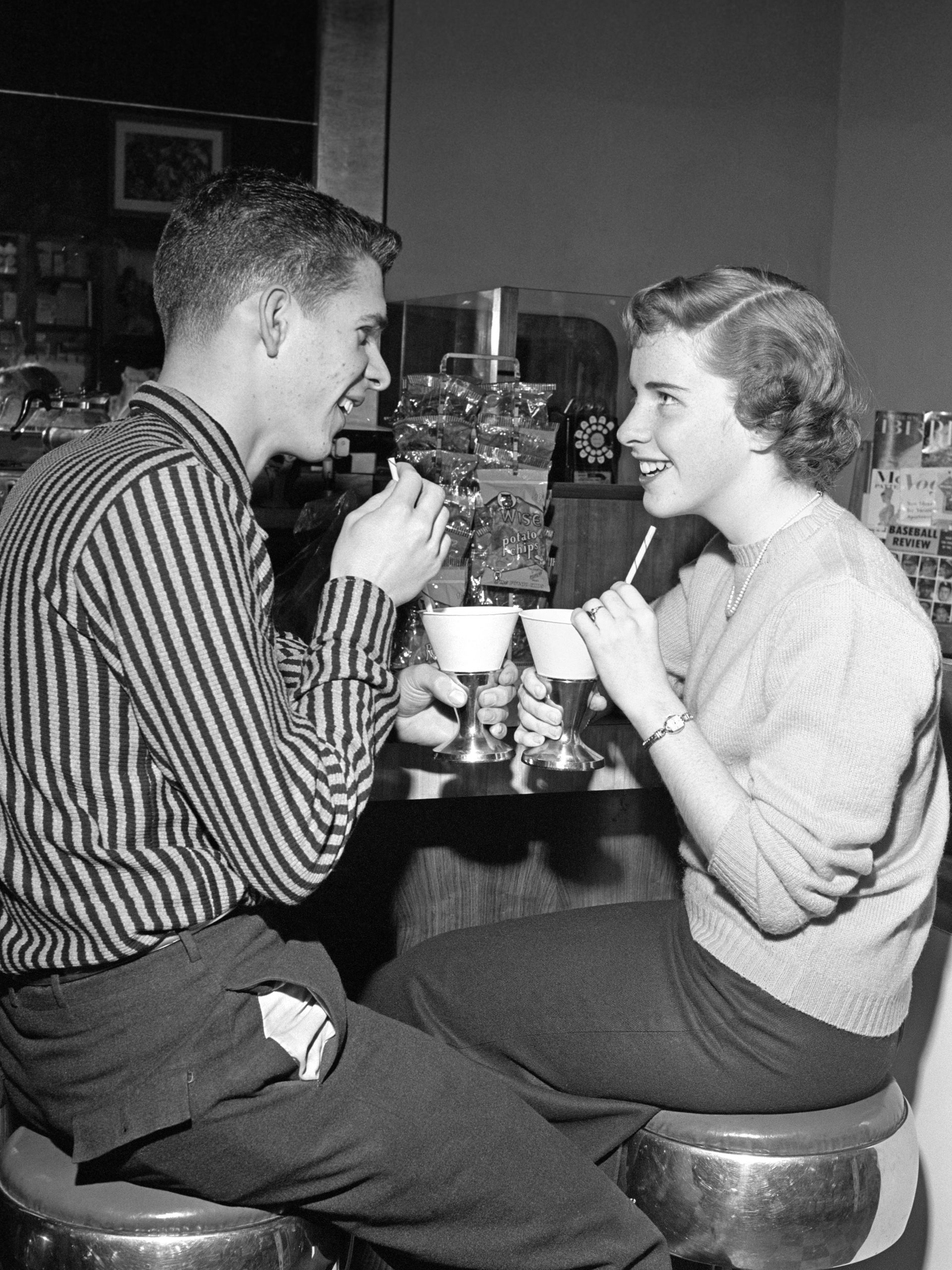
Teenagers in a diner, 1950s
Teenagers in a diner, 1950s
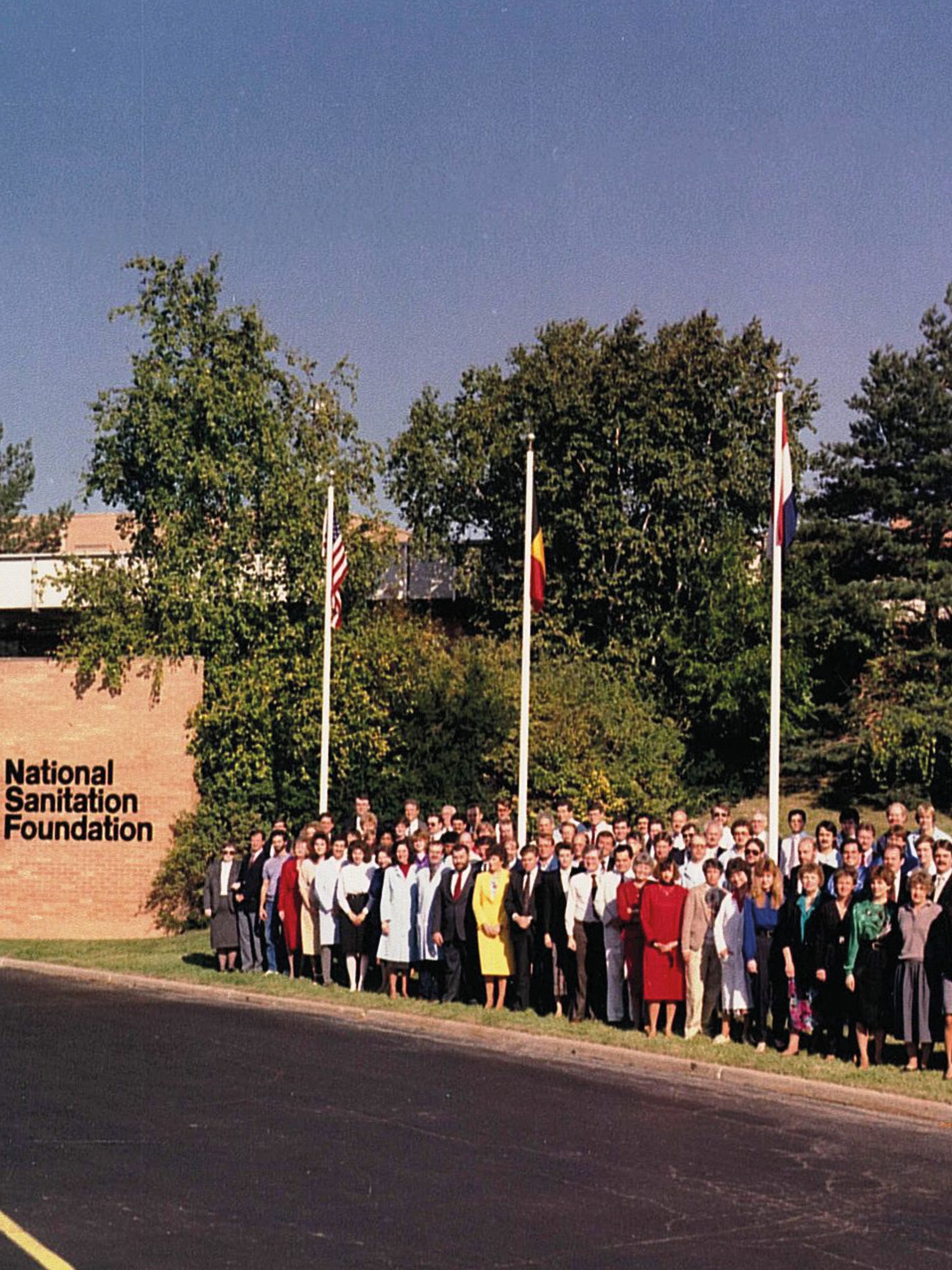
NSF’s orginal headquarters at the University of Michigan
NSF’s orginal headquarters at the University of Michigan
NSF Tradeshow booth, 1950s
NSF Tradeshow booth, 1950s
Passionate public health advocate and former President and CEO Dr. Nina McLelland took the helm of NSF in 1980. Under her leadership, NSF began to expand internationally. A highly respected leader and accomplished scientist, she played an essential role in developing safe drinking water standards that are used worldwide.
Passionate public health advocate and former President and CEO Dr. Nina McLelland took the helm of NSF in 1980. Under her leadership, NSF began to expand internationally. A highly respected leader and accomplished scientist, she played an essential role in developing safe drinking water standards that are used worldwide.
In the 1970s and 1980s, NSF led the development of standards for safe drinking water systems.
In the 1970s and 1980s, NSF led the development of standards for safe drinking water systems.
NSF’s IT hub in Delhi, India
NSF’s IT hub in Delhi, India
Pioneering Public Safety since 1944
In the 1930s, as the United States began its recovery from the depths of the Great Depression, the food service industry started to flourish. The nation’s economic stability slowly began to stabilize; as a result, families increasingly ventured out to eat. A passion for dining outside the home was beginning to take root – and with it came an increased need for better food preparation and preservation practices.
It was 1939 when millions marched off to war. Given the varied conditions under which soldiers would operate, military training was comprehensive, and health and hygiene were paramount. Soldiers were educated about potential health hazards they might face, from tropical diseases to the challenges of maintaining health in the harsh winter conditions of Western Europe. Sanitation in field conditions was a recurring theme; and this military training had a ripple effect. Returning soldiers carried the lessons they’d learned about the importance of cleanliness, and public awareness increased.
However, there was still a long way to go – in the early 1940s, public health officials were well aware that sanitation research had failed to keep pace with new problems resulting from modern living. Health officials in each U.S. state were acting independently of one another; and to make matters worse, they were relying on outdated research. The result was wide variations in the rules and regulations that governed sanitation throughout the country as a whole – the need for consistent practices was evident.
“We have always held to the hope, the belief, the conviction that there is a better life, a better world, beyond the horizon”
The Founding
of NSF
Walter F. Snyder – the primary founding member of NSF – got his start in public health from a small grocery store on Peck Street in Toledo, Ohio. Sanitation enforcement was arbitrary at best – local health officials would come in looking for insects in display cases, or to focus on sawdusting the meat market floor. Frustrated by these inconsistent and half-hearted practices, he took his case to the city officials; they appointed him Director of Sanitation in the Toledo Department of Health. Walter Snyder’s subsequent academic career culminated at the University of Michigan, where he shared his philosophy that public health could best be addressed by bringing together all relevant parties. Two of his fellow faculty members – Henry Vaughan and Nathan Sinai – concurred, and in 1944, they jointly established the National Sanitation Foundation.
NSF went to work, developing hygiene and sanitation standards based on consistent, science-based evidence. NSF convened diverse stakeholder groups – including health officials, regulators, manufacturers, purchasers and permitting agencies – to develop standards of best practice and help eliminate much of the guesswork and inconsistency in design, material selection, performance, and specification of products.
It soon became clear that NSF’s standards and related product certifications were helping to improve human health. Today, NSF has facilitated the development of more than 160 consensus-based standards and protocols. Products certified by NSF to these standards bear the NSF mark, which is recognized by consumers, manufacturers, retailers, and regulatory agencies worldwide.
Pioneering Public Health
“What is needed now is the organization and development of an agency devoted to scientific research in sanitization; an agency that will maintain intimate contacts with national, state and local governments”
“We are proud to be associated with NSF since its very beginnings when a group of scientists from the University of Michigan School of Public Health developed a vision to leverage the best available science to improve public health. We are grateful for NSF’s continued support through multiple scholarships and research partnerships that are central to our mission to develop the next generation of public health professionals and address the biggest challenges to human health.”
Early Food Equipment Standards
The 1950s was a pivotal decade in the realm of food equipment and processing. The post-WWII era saw a massive economic boom and a significant expansion in the food service industry. As it grew, so did concerns about foodborne illness and contamination, and recognition of the importance of sanitation increased.
In 1952, NSF released its initial two food equipment standards. These guidelines specifically detailed the sanitation requirements for soda fountains and luncheonettes. This was quickly followed by the establishment of standards for equipment used both for commercial cooking and to generate hot water, and for dispensing freezers. Throughout the 1960s and 1970s, NSF remained proactive in setting benchmarks for commercial food service equipment, producing more than 20 distinct product standards.
Early Water Product Standards
Throughout the 1950s, the benefits of NSF standards caught the attention of health department officials responsible for public swimming pools, septic systems, and drinking water distribution. These officials asked NSF to develop standards for the uniform evaluation of products in these areas.
Plastic piping technology was just beginning to develop. Quality, health and safety problems were significant. The physical, chemical, and quality issues related to the nascent PVC industry prevented widespread adoption of this emerging technology. Industry leaders recognized the need for independent standards that all stakeholders could support.
NSF Standard 14 proved invaluable to the quality and credibility of the plastics piping industries.
Today, plastics polymer technology industries look to NSF to provide credible standards, through risk assessments and valuable certifications that allow manufacturers to access global markets. It was this impressive track record that provided the platform for NSF’s most significant standards for drinking water additives.
The Safe Drinking Water Act
In 1970, President Richard Nixon established the Environmental Protection Agency to address extensive air, water, and soil contamination across the country. In 1974, Congress passed the Safe Drinking Water Act, which established federal safety rules for drinking water.
It was a crucial decade for both understanding the risks of lead piping for water transfer, and the rise of alternative materials for water infrastructure. NSF’s role was vital, as concerns about water quality and safety took center stage. Plastic pipes were already emerging as an alternative to lead, and there was a need to ensure their safety, especially when used for potable water. By working with the American National Standards Institute (ANSI), the NSF/ANSI standards became the go-to for certifying material used in drinking water systems.
NSF standards 60 and 61 were completed in 1988; today, they are still considered the gold standards for drinking water products worldwide.
“Safe drinking water is essential to the health and well-being of every American. In signing the Safe Drinking Water Act of 1974, I reaffirm my earlier commitments to Congress that improving the quality of life for all our people includes assuring them of safe drinking water. This legislation will assure Americans of standards that are both strict and feasible for the quality of their drinking water.”
The American National Standard for Dietary Supplements
In the late 1990s, dietary supplements emerged as a new trend and, once again, standardization and independent certification were needed to help keep potentially harmful, low-quality products from the marketplace. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) had not yet published its Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs) for the supplement industry, and in 2003 NSF responded by developing NSF/ANSI 173, a voluntary consensus standard for the production, packaging and labeling of dietary supplements.
Recognition by the World Health Organization (WHO)
NSF’s scientific expertise and ability to drive consensus standards in areas of public health led to NSF being recognized in 1996 as a WHO Collaborating Center on Drinking Water Safety and Treatment. In 2014, NSF was designated as a Pan American Health Organization/WHO Collaborating Center on Food Safety, Water Quality, and Indoor Environment. Over the last two decades, NSF has provided secondees to WHO to work on priority projects that include airline water safety; safety plans for small, centralized water utilities; and home water treatment system verification.
Additionally, NSF’s team of expert toxicologists has actively contributed to WHO’s risk assessment initiatives. They’ve been pivotal in revising WHO drinking water guidelines and refined food chemical risk assessments, underpinning the methodologies for chemical risk evaluations in the food sector. NSF remains committed to its strategic partnership with the WHO and is proud of its long-standing relationship with the premier public health organization in the world.
Supporting Health Departments and Communities
Public health officials are responsible for keeping communities safe, but the marketplace moves much faster than any legislation or regulation. Health departments are not staffed, trained, equipped, or funded to conduct thorough technical evaluations of the many products installed.
Over the 80 years since it was founded, NSF has earned the trust and confidence of local, state, national, and international regulators. The most logical method to ensure products aren’t harmful is to request that manufacturers obtain an independent certification by an accredited organization, one which has proven expertise in the field. NSF is known as a reliable and capable certification body, and the trust and confidence of the regulatory community is one of NSF’s greatest assets.
NSF has developed long and productive relationships with state and local regulators, as well as the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, the Food and Drug Administration, the U.S. Department of Agriculture, and similar agencies around the world.
“NSF has produced standards that are in use worldwide and have been highly respected by the U.S. government and by foreign governments.”
International Expansion
In the 1980s, NSF began to establish its presence internationally with the opening of its Brussels office, recognizing the global nature of public health challenges and the interconnectedness of industries across borders. This expansion has grown exponentially – it now operates in 180 countries, from over 45 offices and state-of-the-art laboratories.
Throughout its international expansion, NSF has worked to ensure that its certifications and all standards are recognized and respected globally. It has formed partnerships, alliances, and collaborations with various national and international bodies to establish and promote safety standards across different countries. Crucially, it’s ensured that international standards are aligned with local needs.
Expanding internationally not only allowed NSF to work with clients across the globe, but also to attract and develop bigger talent pools in support of its mission. A good example of this dual approach to internationalization is NSF’s growth in India. NSF built a large IT hub in Gurugram, near Delhi, which supports NSF’s operations worldwide, including application development, remote user support and customer-facing digital solutions, such as NSF TraQtion.
“At NSF, we have embraced what we call a “glocal approach.” We provide the best available science and global best practices to our clients, while tailoring our solutions to the local market needs. A good example is the work we do with the Quick Service Restaurant (QSR) industry. For these customers, providing a consistent customer experience across stores is key to maintaining global brand standards. This requires in turn a deep knowledge of the local market’s dynamics – which are evolving constantly. We’re extending food safety for them beyond a traditional supplier approach and looking deeper at the end service point.”
The NSF
Mark
2
The NSF certification mark is a pledge of assurance, instilling confidence in quality and safety for consumers, retailers, and regulators.


The NSF Mark
The NSF mark is recognized by consumers, manufacturers, retailers, and regulatory agencies across the globe as a symbol of trust and quality; the symbol signifies that a product has undergone thorough testing and has been certified by one of the world’s most reputable independent organizations.
The mark represents several key attributes. Firstly, it tells the consumer that a product has been meticulously reviewed against established standards and guidelines and has passed an impartial assessment process – and this review is in turn subject to objective verification by a third party, instilling confidence in a product’s reliability. And secondly, the NSF mark provides a competitive advantage by setting a product apart from others in the market – it demonstrates an organization’s commitment to maintaining high standards of quality and safety.
“When I joined NSF 19 years ago, I was naïve enough to think that if a store had a product on its shelves, it must be tested, and it must be safe. I learned that this wasn’t necessarily the case. The NSF mark provides peace of mind that independent auditors have visited the manufacturing facilities and assessed how these products are being produced. What gets me out of bed in the morning and ready to take on the day is being able to make a difference in the world, and protect the well-being of my family, my friends, my colleagues, and our environment.”
The Reach
of the NSF Mark
The NSF mark can be seen on a wide variety of essential products worldwide – from the food aisles of your local supermarket to household appliances such as dishwashers and washing machines to food equipment such as refrigerators and coffee machines. Water-related products, including water filters, purifiers and treatment chemicals carry the NSF mark, as do plumbing components such as pipes, fittings, valves and faucets. Many health and wellness products, such as dietary supplements and nutritional ingredients; cosmetics and personal care products also carry NSF’s blue mark.
In 2020, NSF partnered with Wegmans Food Markets to launch its Verified with Confidence program, ensuring that all dietary supplements and CBD-containing products, herbals and probiotics are certified for good manufacturing practices and meet product testing requirements – put simply, NSF assures that what it says on the label, is what’s in the bottle.
“We worked with NSF to launch this program knowing this is the right thing to do for our customers,” said Betsy Crater, Non-food Quality Assurance Manager at Wegmans Food Markets. “We are excited to be a leader in this initiative and help inspire others in the industry to get on board as well.”
A representative sample of the dozens of certifications you will see across the aisles
Find the NSF mark wherever safety and quality matter
• Drinking water
• Home appliances and cookware
• ISO certification at facility level
• Sustainability
• Environmental claims
• Risk assessment
• Food and beverages
• Dietary supplements
• OTC pharmaceuticals
• Cosmetics and personal care
• Medical devices
“Wegmans is demonstrating true leadership with its Verified with Confidence program,” said David Trosin, Managing Director of Health Sciences Certification at NSF. “Consumers want to know what’s in the products they buy, and more and more they are expecting retailers to play an active role in quality assurance and product safety. We envision a future when most major retailers will require brands to show proof of product quality in some form or another, whether through independent assurance of GMP compliance, independent laboratory testing of products, or both.”
NSF is also the exclusive certifier for the Plant Based Foods Association (PBFA) program, available in the U.S. and Canada – a certification and label that make it easy for consumers to choose sustainable alternatives to meat, egg and dairy products, providing assurance that the food contains no animal-derived ingredients. The PBFA promotes growth in the plant-based food industry, working to create a supportive environment for plant-based food companies and advocate for policies that facilitate the development and distribution of plant-based products. Its membership includes a diverse range of companies, from startups to well-established brands, including manufacturers of plant-based dairy alternatives and meat substitutes.
Additionally, NSF’s Certified for Sport® program assists athletes, nutrition experts, coaches and everyday consumers in making safer choices when it comes to sports supplements. The certification is the only one of its kind; and it’s widely respected. Leslie Bonci, Kansas City Chiefs Sports Dietician and Klean Athlete Sports Nutrition Advisor, concurs: “ Certified for Sport® gives both my athletes and myself the reassurance we need that the dietary supplements we choose have been tested and certified for quality, purity and safety.”
Tested for Quality and Safety
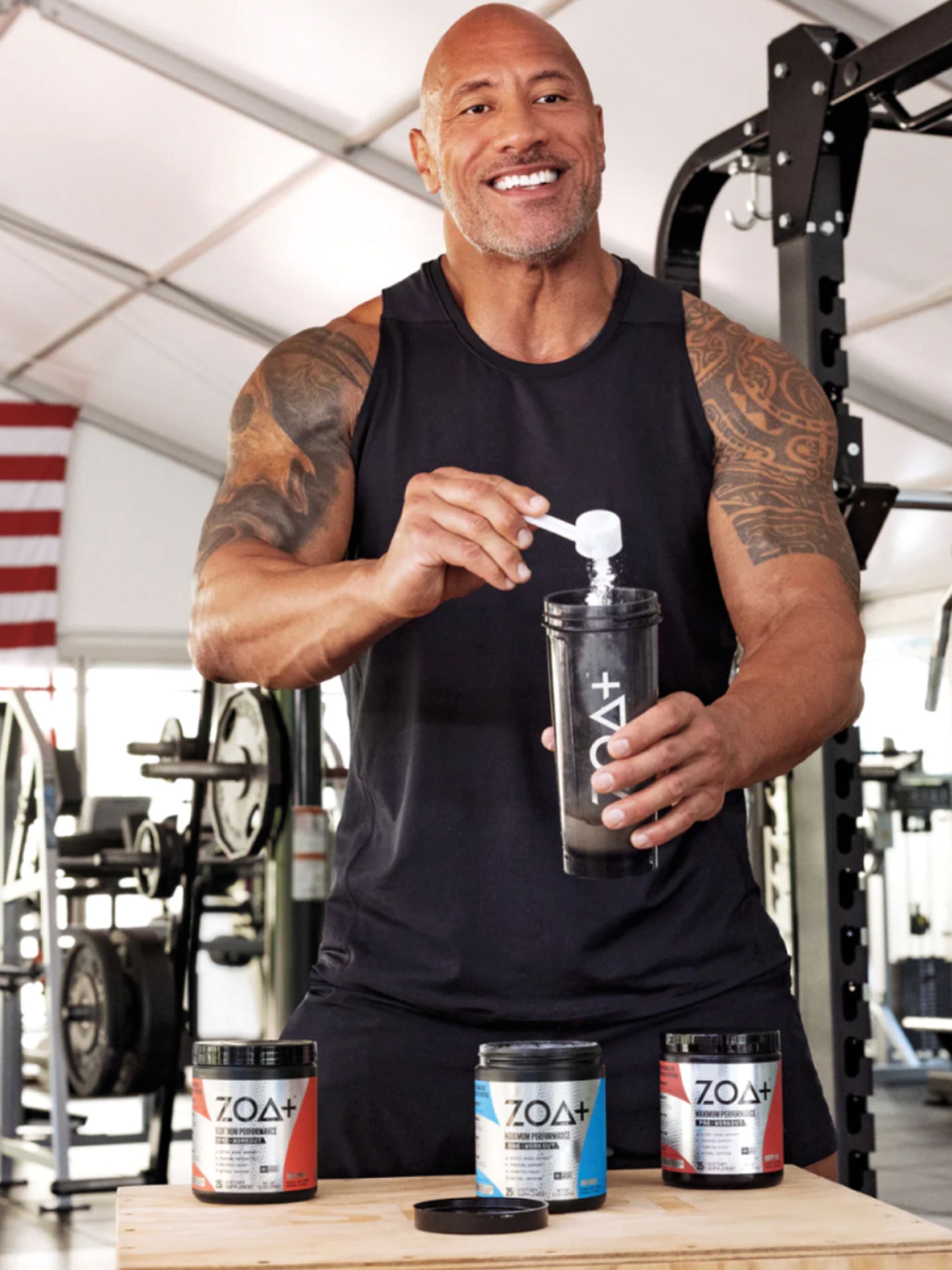
“I’m proud to say that ZOA+ is officially NSF Certified for Sport, which means athletes at any level, across any field of sports, including those overseen by the United States Anti-Doping Agency (USADA), can have peace of mind that when they use ZOA+ powder, they are using a safe and trustworthy product, which is of the utmost importance to me and my co-founders.”
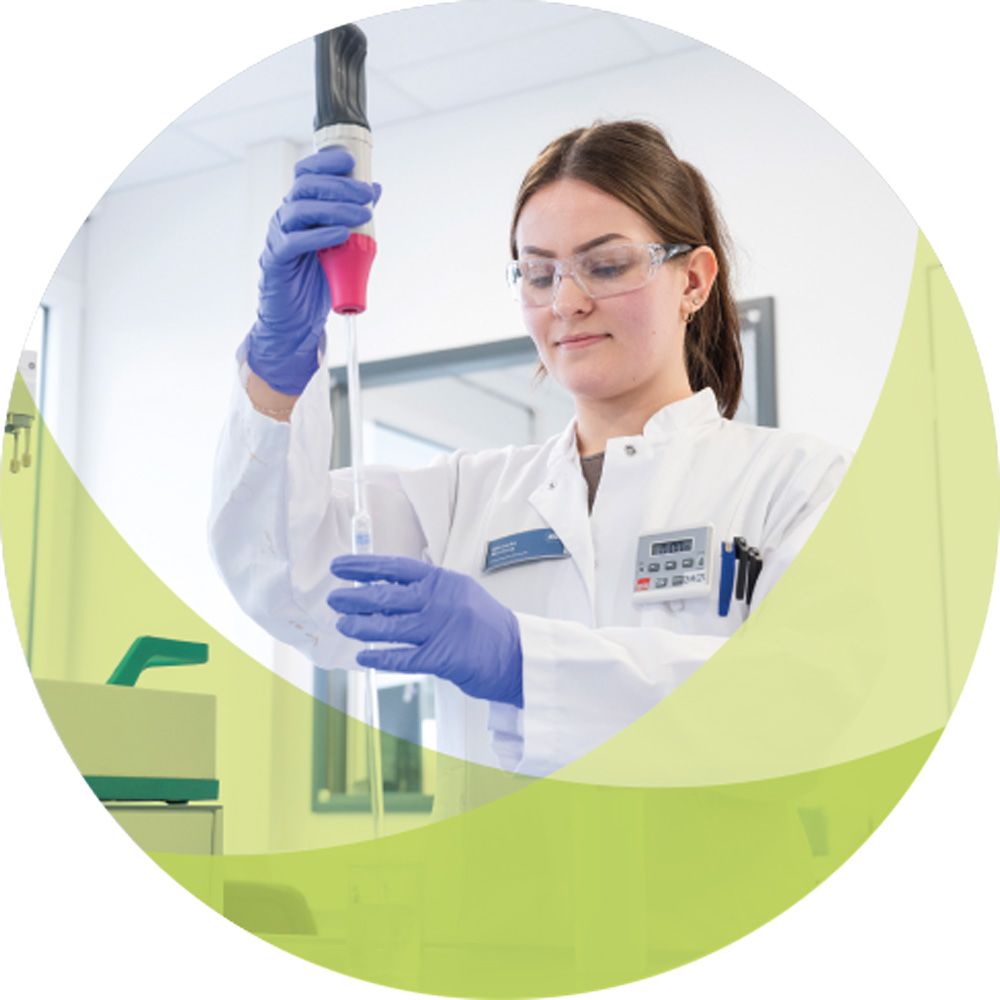
NSF’s Laboratories
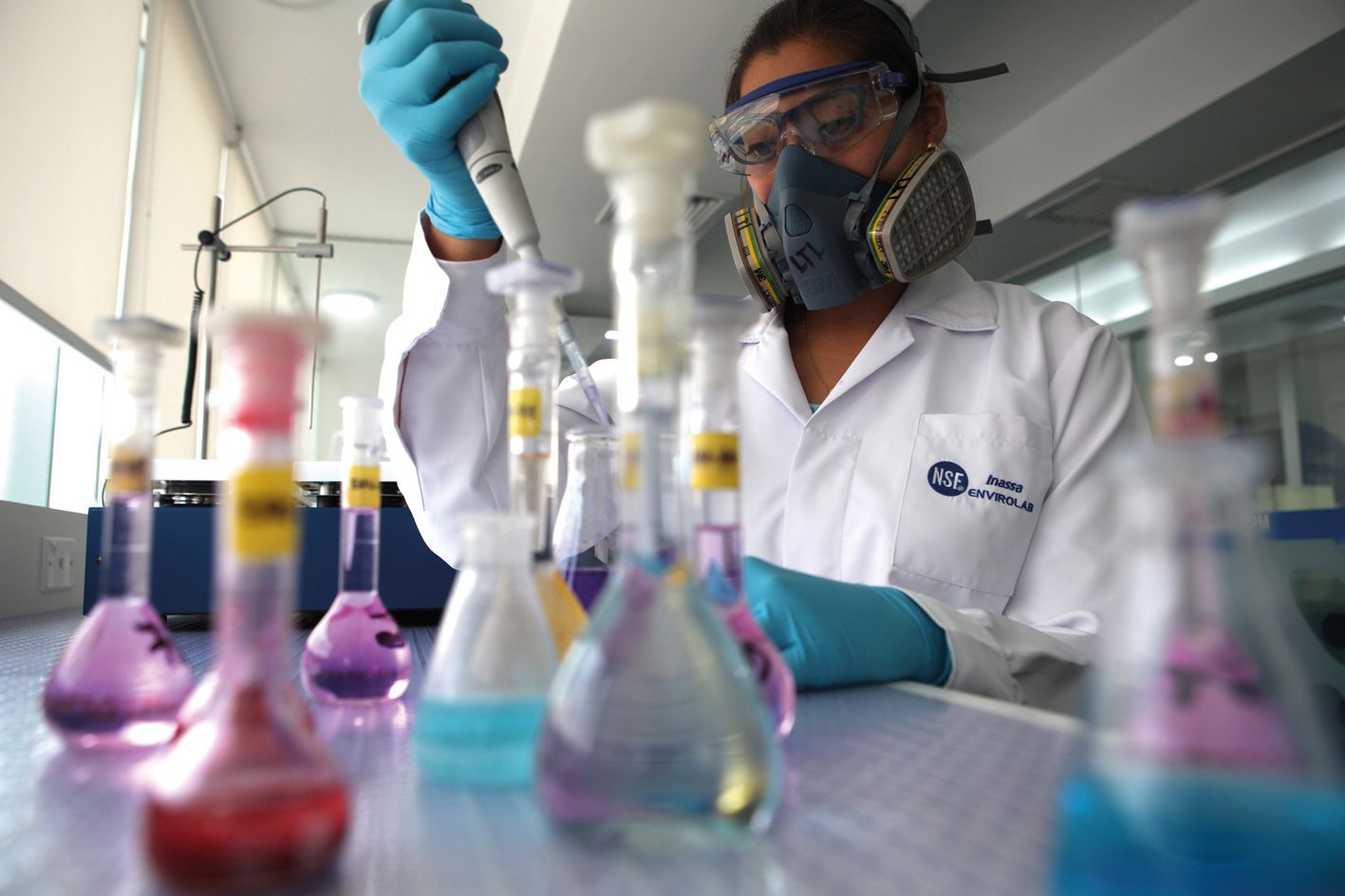
NSF’s network of state-of-the-art, ISO/IEC 17025 accredited laboratories spans across North America, Latin America, Europe, and China. The NSF labs employ a professional staff of best-in-class engineers, microbiologists, toxicologists, chemists, and public health experts. They perform a broad range of specialty testing services including ingredient identity, purity, quality analysis and bioanalytical research.
Scott Morris, Vice President of Laboratories, says, “The testing we do is varied and international, from water testing in Wales and China to food testing in Germany, and we are growing exponentially.
“The NSF mark is everywhere, from refrigerators, to ice machines, bottles of water or shelving units. And it makes me very proud as both a consumer and an employee of the company.”
The NSF mark is a lot more than a label; it represents a commitment to public health, sustainability, and innovation. Whether it’s assuring the purity of our drinking water, certifying the safety of our food, or validating the performance of cutting-edge health products and technologies, the NSF mark continues to be a beacon of assurance for consumers and a source of pride for manufacturers worldwide. Its significance is deeply rooted in the pursuit of a healthier, safer, and more sustainable future.
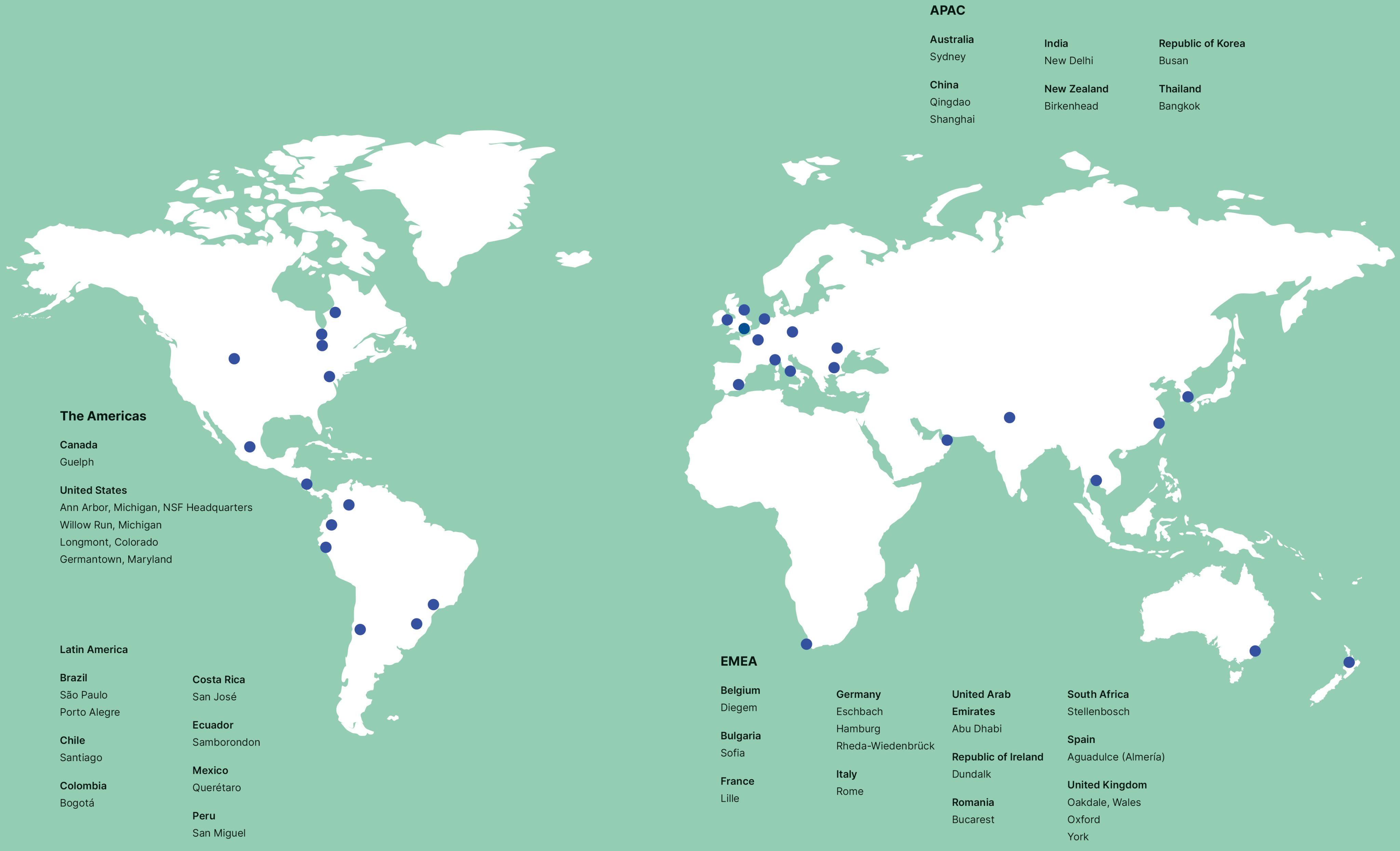
NSF Global Footprint
Serving 40,000+ clients from 45+ offices and state-of-the-art laboratories
World-Class Talent
3
People are at the heart of NSF, driven by a mission to improve human and planet health.


World-Class Talent
As a global services organization, NSF boasts a remarkable team of more than 3,000 highly skilled professionals. NSF aspires to connect with, hire and provide equal opportunities for skilled individuals who represent the diverse customer base and society the company supports.
Spanning the organization’s three core areas – food, water, and health products – the demands on the team are both diverse and intricate. To thrive at NSF, team members must bring a comprehensive set of technical and leadership skills to the table, reflecting the multifaceted nature of NSF’s work.
“As a leading services organization, our people are literally our main asset. My role is focused on the overall development of our team members – encouraging their growth and career progression. It’s fun and fulfilling to be part of a team that is dedicated to support our team members grow and make an impact in the world.”
“What motivates me to work for NSF is its compelling mission of protecting human health and I truly believe that we can make it happen. The best thing about my job is working with NSF’s wonderful people. I love to work together to develop new strategies and grow our business in the Latin America region. I believe that we can make a difference in people’s lives, which is very energizing.”
For Chiara Destino, a Senior Regulatory and Labeling Consultant based in Belgium, it’s the focus on human health – combined with the international nature of her work – that inspires her: “It’s important to me to work to the highest ethics and quality so that all consumers can easily and clearly find the necessary information on a food product without being misled. For example, being certain of which allergens a product contains can be of vital importance for some people, and I guide our customers to design labels in accordance with national and European regulations. Because of my language skills, on top of my scientific and legislation knowledge, I am able to cover a wide range of scopes and it gives me satisfaction to use these skills daily, building great relationships with customers and collaborating with NSF colleagues across the globe.”
Our World-Class Talent
Donald McFarland, Technical Manager, Aerospace, enjoys working with the major names in the Aerospace sector which he grew up hearing about: “The thing that attracts me the most to NSF is the access to flagship clients. I was born at the Air Force Academy and have been in the aerospace world my entire life. Working for NSF has allowed me to visit the key players involved in aerospace, helping them to evolve and drive continued improvements across their business. I also love working with the NSF team – they’re wonderful people. The leadership has been very inspiring, and they really listen to all ideas.”
Sarah Krol
Sarah Krol
Sarah Krol, Vice President, Food Supply Chain, has been at NSF since 2005, and is responsible for the strategy, growth and execution of NSF’s global food safety services, focusing on the early segments of the food supply chain. This includes growers, animal production, seafood operations, processing, packaging storage and distribution. Sarah and her team provide industry recognized and bespoke food safety audits that protect the safety, quality and integrity of the food supply chain, also providing differentiating certifications and verifying food label claims.
“I worked in pharmaceuticals and biotech for about seven years after college, so I was familiar with pharmaceutical testing and FDA lab requirements. I started at NSF as an entry-level Quality Specialist and have been fortunate to have a wide range of experiences at NSF that have ultimately led to advancement within the organization. NSF has continually grown and evolved, so in a sense I’ve never felt like I was working at the ‘same’ company. With NSF I have had exposure to formative experiences – traveling the world, engaging with senior leaders, sharing in customer experiences when they achieve NSF Certification and can go to market with their product. Perhaps most of all I enjoy the people here that make up NSF – those I’ve helped develop to take senior roles in the company and those that have left to become our customers in some cases. I have the best peers and have been led and mentored by amazing and diverse senior leaders – it’s been incredibly rewarding.”
Within NSF, there are various specialized areas, each playing a pivotal role in operations. Certification specialists are instrumental in the evaluation and certification of products, processes, and systems, ensuring that they have compliance with industry-specific standards and regulations. Meanwhile, globally renowned toxicologists assess the safety of chemicals, ingredients, and products, diligently identifying potential risks to both public health and the environment. NSF scientists are indispensable to the company’s achievements.
“The value of the instrumentation we have in our laboratories is somewhere in the $50 million range,” says Scott Morris, Vice President, Laboratories. “So they’re well capitalized, and state-of-the-art. It’s true science, what we do; and for it to work, we can’t just have people that push buttons and have a production process; we need solid scientific talent to enable us to be successful.”
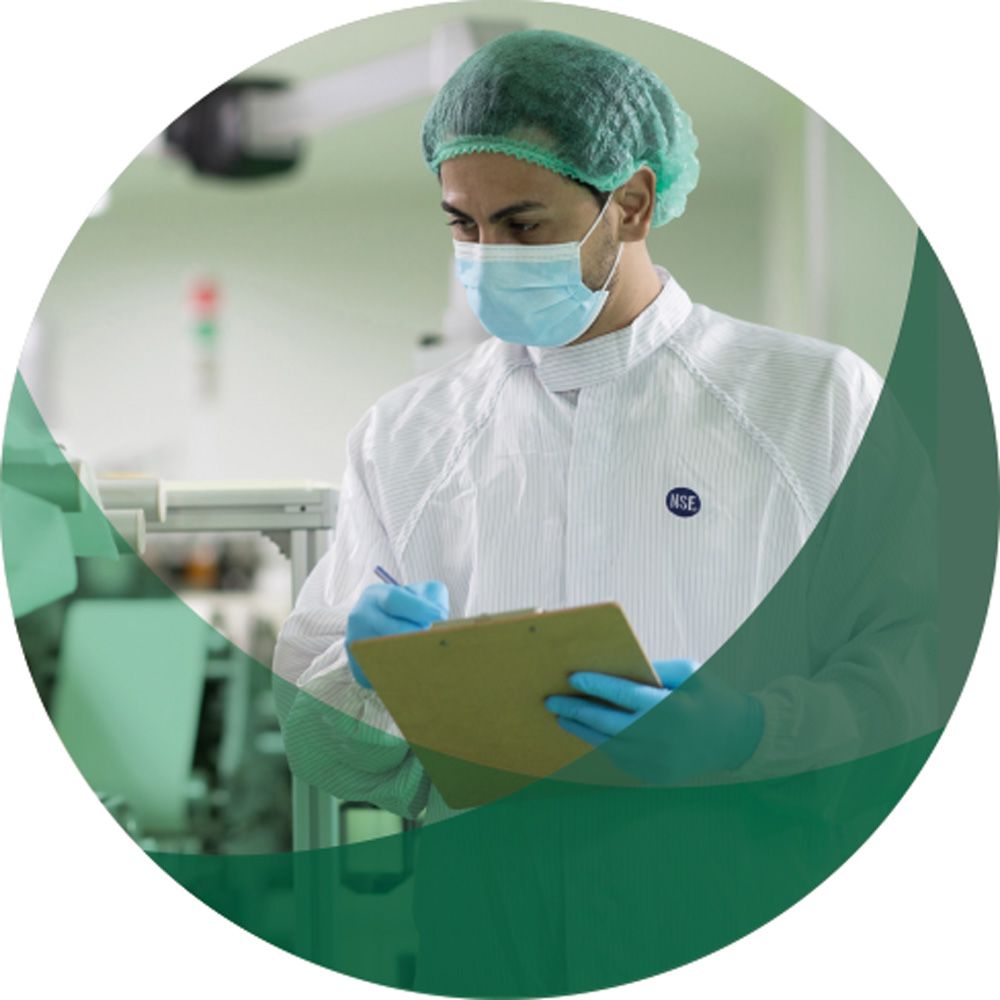
Auditing is an essential part of NSF’s work, evaluating whether a process or a facility complies with relevant regulations, standards, and best industry practices, as well as conducting on-site inspections and data collection.
“I have a passion for making sure the auditors are doing a thorough, robust job,” says Leon Ford, Lead Auditor for third parties at NSF. “We are a client-facing service, whilst being independent. And every day is different – there’s not been one in my seven years of auditing that I’ve failed to learn something new. My best moment with a client was an audit that I did which was four and a half days long, so there was a lot of complexity and potential for things to go wrong. When they realized they had got provisionally the best grade that they could, they all cheered and there were tears of joy. It’s really rewarding as an auditor, that you can deliver that.”
South Korea-based auditor Eric Hyungyu concurs: “My goal in life is to make people around me happy, so I was attracted to this role because of that. My job helps keep food and therefore people safe, not just in Korea but all around the world.”
Inspired by Purpose: Vikas
NSF’s commitment to maintaining a world-leading international workforce, and recruiting the most promising experts of the future, is crucial to the company’s success – as is employee happiness. India-based Vikas Yadav says, “I’m a Support Technician at NSF. I help staff with their day-to-day issues on their computers. What best sums up what I bring to my work is being helpful. I wanted to work with an organization that would give me international work exposure. To work for NSF you must be motivated, polite, and happy to help people.”
Cultivating a high-purpose, high-performance culture is crucial to NSF’s continuing success and growth. The foundation of this is NSF’s four core values: Doing the Right Thing, Treating People Well, Relentlessly Pursuing Excellence, and Working as One NSF.
As a leading public safety company, NSF is committed to ensure the safety and wellbeing of its team members, so they all get back home to their friends and family the way they came to work. In 2023, NSF formalized its commitment to ‘goal zero’ – this means zero accidents across NSF globally, and this is now embedded in everything the company does.
Inspired by Purpose: Sutida
NSF’s leadership framework was founded in the belief that everyone at NSF is a leader, and so investment in building leadership skills at all levels – and nurture the next generation of leaders – is a mission-critical imperative.
NSF is committed to being a great place to work, by providing the opportunity to do meaningful work alongside inspiring colleagues, to grow and develop and also, to have access to competitive, performance-based compensation. The company solicits team members’ feedback regularly through structured engagement surveys to take the pulse of the organization and better address the evolving needs of its diverse team members.
Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI) is a bedrock of NSF’s talent strategy. NSF’s DEI program slogan is “It takes everyone” because it values everyone’s perspective and encourages everyone to be their authentic self at work.
NSF team members are not only experts, but also innovators. The company’s culture and history thrive on new ideas that continue to improve human and planet health, harnessing the ideas of the company’s brilliant talent and bringing them to fruition.
“Each day I think, I want to learn something new, I want to be better, for myself and my team – that’s how I feel every morning. I am proud to be part of NSF. I see myself as a big sister, sometimes even a mother, because I must take care of my team. I work with people – that’s the heart of doing business here.”
Our Mission
in Action
4
NSF plays a crucial role in keeping us safe and healthy in three essential areas: food, water, and health products.


Our Mission in Action
NSF plays a crucial role in keeping us safe and healthy in three essential areas: food, water, and health products. With its 80 years of experience and commitment to thorough testing and high standards, NSF ensures that the food we eat is safe, the water we drink is clean, and the health products we use meet top-notch quality and safety criteria.
Water
Since the company’s formation, NSF has been a driving force in the water industry, tirelessly working to ensure clean and safe water for all. Whether it is ensuring drinking water safety, discovering innovative wastewater treatment methods, or safeguarding water resources, NSF has been dedicated to improving water quality and conservation.
NSF’s expertise in water safety was evident during the Flint Water Contamination crisis, when the City of Flint, Michigan decided to switch its municipal water supply to the Flint River in April 2014. This change led to the corrosion of water distribution pipes, resulting in the release of lead and other harmful substances into the drinking water. As a response, residents of Flint were advised to avoid drinking tap water unless it had been processed through an NSF-approved filter, certified to eliminate lead. NSF played a pivotal role during this crisis by offering its expertise and guidance to government officials, and engaging directly with the community, providing reassurance and advice to anxious residents.
Our Mission in Action
With consumers increasingly aware of the dangers of contaminants in drinking water, demand has grown for residential filters. NSF has developed numerous standards across the water cycle (municipal, residential, wastewater) and an independent certification program to help the credibility, safety and performance of drinking, recreational, waste and reuse water treatment products. Today, those standards and certifications still provide unparalleled reassurance to consumers.
NSF’s expertise in water safety is also exemplified by the work it does with Westlake Chemicals, which produces Accu-Tab® chlorine tablets, a product that has undergone rigorous, independent evaluation by NSF. This thorough testing process ensures that these tablets consistently meet the demanding quality and safety standards set by NSF. Accu-Tab® chlorine tablets are the exclusive choice for Accu-Tab® chlorinators.
Dave Purkiss
Dave Purkiss
“There are two types of chlorine tablets – two different chemicals that can be used – and there’s potentially two problems,” says Dave Purkiss, Vice President, Water at NSF. “First, if you inadvertently mix the two different chemicals, it could potentially cause an explosion; and second, chlorine tablets are formulated to dissolve at a specific rate, so there’s a risk of over- or under-chlorinating the water if they’re incorrectly applied. We identified a need to address these crucial safety issues, and then worked with the industry to develop a standard that addresses the certification of chemicals and chemical feeders. Westlake worked with NSF to really promote this issue across North America, and got the requirements written into several state pool regulations. It’s really educated the recreational water community about the importance of using the right chemicals with the right feeder.”
Frank Schiffman, Business Manager and Marketing Director, Westlake Chemical:
“At Westlake, and within our Water Solutions business in particular, safety is our core value. It translates into how we work, and our quality processes; which in turn translates into adherence to NSF/ANSI standards.
“Our equipment and chemical products are designed to deliver chlorine and dry acid to meet specific commercial and industrial applications. They are designed to help maintain pathogen-free and balanced water according to individual requirements. NSF certifies our Accu-Tab® and Acid-Rite® feeders and tablets to those standards. That way we know that we’re telling our customers (and their customers) that Westlake units are going to perform according to testing that’s universally recognized and trusted.”
“EcoWater makes a wide variety of drinking water treatment products. We have chosen NSF as our certification organization primarily because of the reputation it receives from our customers. Many of our customers actually require that we be certified by NSF. I’ve been very happy with my program manager whom I work with at NSF.”
Food
Since the early formation of the company – when NSF developed standards 1 and 2, which covered sanitation requirements for soda fountains and luncheonette equipment – the company has continued to create standards to meet changing requirements across all aspects of the food industry, from commercial cooking and warming equipment to hot water generators and dispensing freezers.
NSF places a strong emphasis on food safety. This commitment was particularly evident when the E. coli pathogen, typically associated with undercooked meats that poses a potentially fatal risk to humans, emerged in the 1990s. In response, NSF took proactive measures by creating a food safety and quality committee comprised of key federal regulatory bodies and food industry leaders to innovatively combine the prevailing HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point) food concept – a way of managing food safety hazards – with the rapidly growing ISO (International Organization for Standardization) 9000 quality management system, and the new HACCP-9000 food safety system was born: - a new global standard for food quality and safety still in place today. This established food safety expertise extends across many sectors, encompassing agriculture, animal feed and welfare, and seafood as well as the retail and restaurant industries.
What our Clients Say
As consumer values focus on the well-being of animals in the food supply chain, the NSF Global Animal Wellness Standard (GAWS) helps companies take an holistic approach to animal wellness. The standard requires assessing the health and welfare of animals as well as the environment, physical conditions, provision of feed and water, and appropriate handling to ensure the emotional well-being of the animals.
Launched in 2019, GAWS is the first system in the food agriculture industry which establishes a universal approach; and it offers industry producers and buyers an outcome-based solution that addresses the entire lifecycle of all key species. Saudi Arabia-based company Almarai was the first company to be certified to GAWS for dairy production in the world, and the first company in the world to be certified for poultry production in the Middle East. GAWS aligns with Almarai’s sustainability strategy, Better Every Day, which focuses on caring for consumers, protecting the environment and producing responsible products.
“Almarai is one the most trusted food companies in the region and is known for its product quality. We place great importance on animal welfare. Not only because it’s the right thing to do, but also to help ensure consistent high quality and safer products. NSF has been hugely supportive throughout the whole process, which enabled us to set up and aligned our animal welfare management system to the latest international standards.”
Health Products
NSF helps to ensure the highest level of quality and regulatory compliance for a large range of health-enhancing products – from nutritional supplements to cosmetics, medical devices, vaccines or biotechnology compounds.
As the consumption of dietary supplements continues to grow, it has become imperative to prevent adulterated and potentially hazardous products from entering the market. In light of this demand, NSF created NSF/ANSI 455-2, a set of rules that helps ensure products like vitamins, dietary supplements, and other health-related items are safe to use and actually do what they claim to do. NSF/ANSI 173, a standard that checks if food products are labeled correctly, confirming that the information on food labels, like ingredients and nutritional facts, is accurate and matches what’s in the product.
Since its introduction to the U.S. market in 2004, Certified for Sport® has grown into a globally recognized program, educating elite and amateur-level athletes across four continents. It’s designed to help athletes avoid banned substances in adulterated sports drinks, bars and supplements. The program requires lot-by-lot testing for over 290 substances banned by the World Anti-Doping Agency and leading sports organizations, such as the National Football League (NFL) and Major League Baseball (MLB). In addition, products bearing NSF’s Certified for Sport® mark must be produced in a manufacturing facility that is inspected twice a year to comply with Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) requirements.
“My health and my body are my biggest assets. I need the highest possible level of safety and the assurance that everything I take is clean and tested.”
Major League Baseball is the first major professional sports league to form a sponsorship agreement with a CBD company, Charlotte’s Web Holdings, the market leader in hemp-derived CBD products. Charlotte’s Web is now the first “Official CBD of Major League Baseball.” In June 2022, MLB officially opened the category for the league and its Clubs, allowing sponsorships with CBD companies that are NSF Certified for Sport®.
NSF Certified for Sport: Charlotte's Web
“As a leader in the CBD category, with products that provide health and wellness benefits, Charlotte’s Web is a welcome addition to the MLB family, representing a landmark partnership in baseball and sports,” said Noah Garden, MLB Chief Revenue Officer. “Charlotte’s Web products which receive the NSF Certified for Sport® designation have met the highest safety standards and can be promoted across MLB events and media platforms. We are excited about the possibilities this partnership offers as CBD becomes a more widely adopted part of the health and wellness regimen of our players
and fans.”
The United States Anti-Doping Agency (USADA) is a non-profit organization responsible for promoting clean and drug-free competition in sports through education, testing, and anti-doping initiatives to ensure athletes’ integrity and fair play. “USADA has always recommended that athletes use only dietary supplements that have been certified by a third-party program that tests for substances prohibited in sport. USADA currently recognizes NSF Certified for Sport® as the program best suited for athletes to reduce the risk from supplements.” U.S. Anti-Doping Agency website, Dec. 11, 2023.
NSF also launched the first cosmetic verification service in 2017, providing customers with the assurance of quality, safety and compliance of their cosmetic products. The U.S. Congress recognized the need to regulate this industry with the passage of the Modernization of Cosmetics Regulation Act (MoCRA) at the end of 2022, which represents the largest change to cosmetics regulations since the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act of 1938. NSF is working with the FDA to leverage the NSF/ANSI 455-3, Cosmetics Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs) as the fastest pathway to enable the new regulation across the cosmetics industry.
In addition to the crucial work that NSF does testing and certifying nutrition and personal care products, NSF provides regulatory compliance, training and clinical research services to the pharmaceutical, biotechnology and medical devices industries, enabling the development and launch of lifesaving treatments and technologies.
ESG and
Sustainability
5
Sustainability is a natural extension of the work NSF does to improve human and planet health.
ESG and Sustainability
NSF’s commitment to planet health is demonstrated through the areas in which we operate and the impact of our services. Our core activities – enabling safe and sustainable food, clean water, and health products for all – support the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) principles are naturally integral to NSF’s core business strategies and decision-making processes, fostering a culture of transparency, accountability and ethical standards.
Our Commitment to Human and Planet Health
Lisa Spicka de Bevacqua
Lisa Spicka de Bevacqua
“It is an absolute joy to lead our sustainability efforts at NSF. Our mission is to enable our clients’ sustainability journey to improve human and planet health. Their success is our success because we share the same world.”
Environmental Responsibility
Environmental responsibility for NSF includes two aspects. First, we are dedicated to reducing our environmental footprint by focusing on the areas where there is the most impact. In addition, NSF is also committed to helping clients achieve their sustainability goals through carefully identifying and incorporating relevant and impactful ESG services.
Our climate efforts strive to reduce Greenhouse Gas (GHG) emissions and water use in NSF’s offices, laboratories and workforce travel. NSF has implemented an Environmental Management Systems (EMS) policy, grounded by environmental targets and objectives that strive to meet and exceed pertinent environmental laws, regulations and other applicable requirements. We have publicly committed to the Science Based Targets initiative (SBTi), and are tracking our scope 1, 2, and 3 GHG emissions to identify emission drivers, set reduction targets, and monitor and report our carbon emissions globally. Waste diversion strategies are implemented across NSF offices to decrease landfill contributions, secure safe disposal of chemicals, and mitigate toxic runoff and hazardous waste within our labs.
NSF creates a positive impact or ‘handprint’ as we work across the food, water and health sciences industries to develop more sustainable operations. Whether it is helping clients conduct life cycle assessments, reduce the scale of deforestation, build robust cybersecurity, enable water reuse in buildings and recyclable medical device components, verify sustainable seafood practices, or enact animal wellness programs across their supplier base, NSF is committed to improving the health of the planet we humans call home.
Social
Social responsibility manifests in a variety of ways at NSF, including employee health programs, DEI (Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion), stakeholder engagement on public health, and our corporate social responsibility through the NSF Cares program.
First, the health, safety and wellness of NSF team members is prioritized through safety initiatives, medical benefits and various team member assistance programs. In 2020, NSF introduced its World Mental Health Day, allowing all team members to take the day off to prioritize their well-being.
NSF’s comprehensive Diversity, Equity and Inclusion (DEI) program supports a healthy and supportive working environment through Business Resource Groups, an active DEI council, employee development opportunities and celebration of global holidays across locations.
Through stakeholder engagement, NSF works collaboratively with standards development organizations, government and regulatory bodies, trade and industry associations, and local communities and universities to shape best practices and effect positive change within the communities where we operate.
The NSF Public Health Council (NSF-PHC) peer reviews and ratifies NSF standards, providing invaluable input, final review and acceptance to ensure that standards protect public health. NFS-PHC membership includes only representatives from government/regulatory, academia, public health and public service; there is no industry representation.
The NSF Health Advisory Board (HAB) is comprised of expert toxicologists and risk assessors from government, academia and industry and establishes critical scientific methods used to assess chemical risks to human health. “I have been extremely fortunate and honored to serve as the Chairman of NSF Health Advisory Board, which consists of a robust multidisciplinary team of experts responsible for conducting peer review and promoting the best available and defensible science while addressing emerging technical issues and challenges related to human health risk assessment basis for NSF criteria and standards,” said Dr. Edward Ohanian, Associate Director for Science, EPA Office of Water.
NSF’s long history with the University of Michigan School of Public Health continues; NSF has endowed a faculty position at the school and has established scholarships for international students to help expand public health education around the world.
The NSF CARES committee, comprised of volunteer employees, supports NSF-sponsored charitable activities, including working with non-profit organizations such as Food Gatherers, the Women’s Center of Southeastern Michigan, the Shelter Association of Washtenaw County, Safehouse Center – Domestic Violence Services, United Way for Southeastern Michigan and the Humane Society of Huron Valley – Ann Arbor.
“Women constitute more than 60% of NSF team members and hold around 55% of leadership positions. In order to support them and build allies across NSF, we created an employee-led and company-sponsored Business Resource Group called WIN for Women’s Initiative Network.”
Governance
NSF ensures strong corporate governance through its two independent boards, ESG Council and robust financial controls and reporting mechanisms, as well as independent third-party audits and accreditations.
An area of growing importance is supply chain and data security – both within NSF, and when working with clients. NSF provides ISO/IEC 27001 certification, which defines requirements for establishing and maintaining an information security management system, identifying business risks, building internal awareness and providing a comprehensive international set of controls. NSF is itself independently certified to ISO/IEC 27001, which is renewed on an annual basis and requires stringent internal information security systems to protect company information.
“NSF leverages the knowledge and experience of our two independent boards to help us strengthen our corporate governance and drive our operations with integrity and accountability.”
“Both internal and external audits help to ensure that NSF’s global financial controls are fully operational, underscoring the integrity of our financial operations. Both the internal and external audit teams report directly to the Audit and Finance Committee of the Board of Directors, which ensures that independence and competence are at the forefront of our corporate governance.”
Innovation
6
NSF has been constantly innovating and developing in its three key focus areas of food, water and health products.
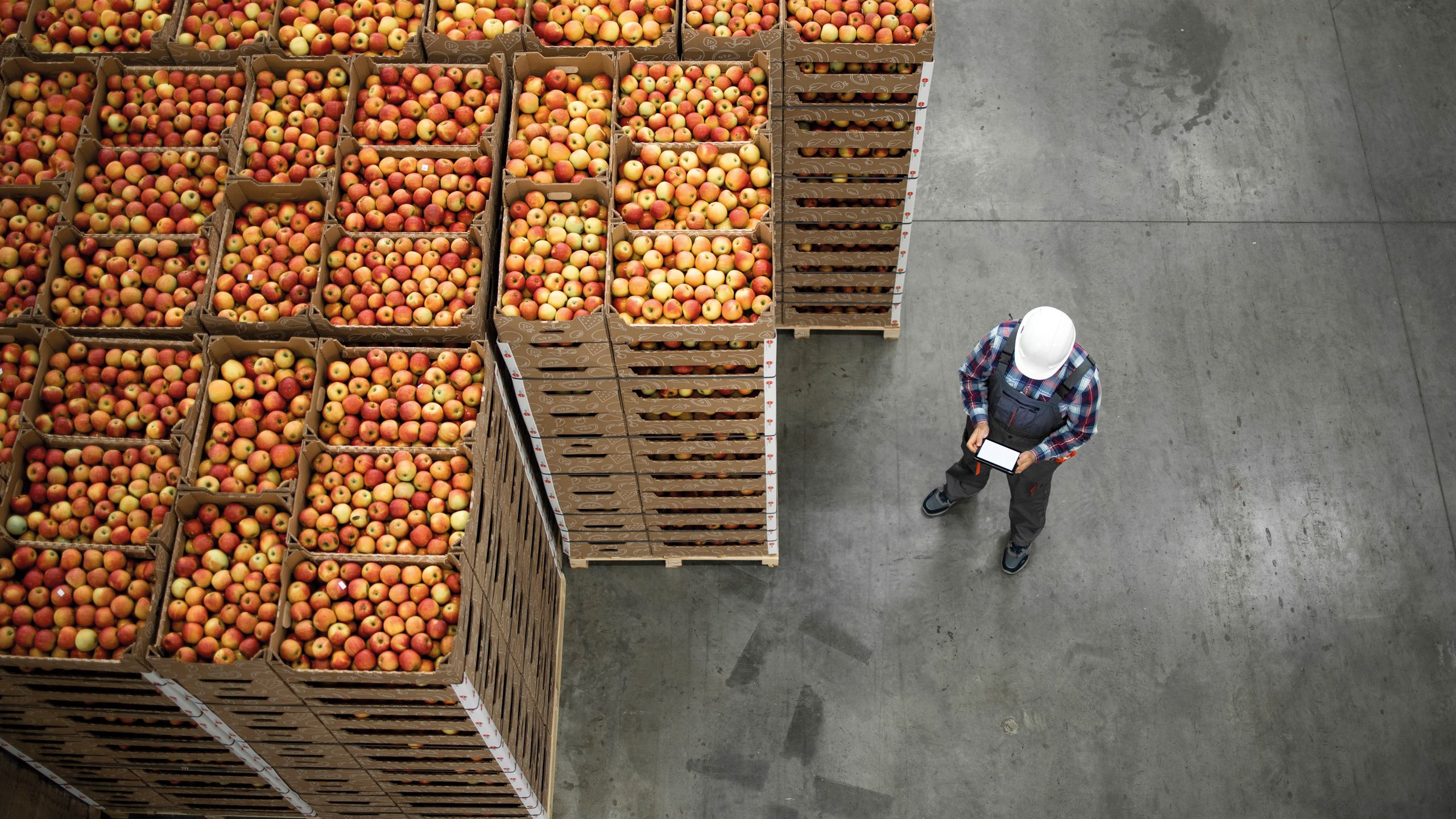


Innovation is in NSF’s DNA
Since its formation in 1944 – from establishing the first two food equipment safety standards in 1952, to the first U.S. national standard supporting the Safe Drinking Water Act in 1980, and then introducing a dietary supplement certification in 2001 – NSF has been constantly innovating and developing in its three key focus areas of food, water and health products. NSF continues to both anticipate developments and react to a rapidly-changing world, looking to the future in its approach to both its own internal practices and the ways in which it supports its clients.
The development of standards and guidelines for a wide range of products and services provides a framework – and companies must innovate to meet or exceed these requirements. Additionally, NSF’s engagement with research and development initiatives addresses emerging challenges in sanitation, health and environmental sustainability; and NSF also offers training and educational programs to help foster a culture of continuous improvement and innovation.
Third-party certification brings credibility to NSF’s clients, enabling them to reinforce their values. Recent studies by Nielsen on the Conscious Consumer Spending Index found that about 73% of consumers want to change their consumption habits to reduce environmental impact. Label claim certifications for products such as organic, plant-based, vegan and non-GMO help brands connect with these conscious consumers. Ultimately, certification gives brands a competitive advantage, as consumer behavior favors brands that can demonstrate their values align with their own.
NSF continues to innovate with new testing methods and certification programs to stay one step ahead of emerging risks to human and planet health – from the NSF CBD and Hemp Product certification which addresses all hemp-based products, to NSF’s Global Animal Wellness Standard, the first of its kind, which offer a consistent, global approach to animal wellness.
The EU and U.S. governments are recommending new safeguards for drinking water; specifically, they’re testing communities across the globe where levels of polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) – manmade chemicals used in waterproofing and non-stick cookware, known as ‘forever chemicals’ because they remain in the environment – are at dangerous levels in drinking water. NSF is part of a joint committee that maintains the American National Standards for drinking water treatment; to comply with the standards, a water filter must reduce the concentration of these PFAS chemicals to below the health advisory standards set.
Microfilter, one of the top companies in South Korea’s water filtration sector, has earned NSF/ANSI 53, becoming NSF’s first client in the world to receive this certification for total PFAS reduction. It produces and distributes high-quality water filters for both home and business applications. “Microfilter is proud to be the first company to achieve NSF/ANSI 53 for chemicals for total PFAS reduction. ‘Forever chemicals’ have been linked with cancer, fertility issues and weakened immune systems, posing a growing health threat to our communities through drinking water sources. We look forward to partnering with companies that share our vision of a cleaner and healthier world. Together we can make a big difference in the fight against PFAS and help ensure a safer and more sustainable future,” said Park Chan-ho, CEO of Microfilter.
Digital Innovation
NSF digital solutions empower businesses to manage supplier data, audits, ingredients and specifications, and to allow access to critical information when it’s needed the most. It enables clients to build an information security framework or raise quality standards with wearable technology.
NSF is constantly encouraging its team members to engage with new concepts. The NSF Innovation Hub, a space dedicated solely for the purpose of brainstorming and idea-sharing, was recently launched at NSF’s Ann Arbor office; it encourages team members to meet, talk, and collaboratively develop new ideas – it’s a space of innovation and creativity, where everyone, and every idea, is welcomed.
Keisha Francis
Keisha Francis
“NSF’s technology brings continuous improvements
to the quality of our audits. We understand the importance of a thorough assessment and how information and analytics go hand in hand. The enhanced capability to provide clients with real-time data that is user-friendly, value added and most importantly enables meaningful insights for smart decision making is a key differentiator for us.”
NSF TraQtion
NSF’s TraQtion™ software is a trusted, cloud-based Software as a Service (SaaS) solution. It’s designed to help businesses manage and ensure the quality and compliance of products and supply chains. Specifically, it’s focused on helping companies streamline their quality assurance and supplier management processes.
The software enables organizations to plan, schedule and conduct audits and inspections of their facilities and suppliers. It helps identify and address non-compliance issues. In addition, the platform facilitates management of documents related to quality and compliance, helping to maintain a centralized repository of critical information.
Customers can access the software through web browsers without the need to install or maintain it on their own servers or devices. As an SaaS application, NSF’s TraQtion™ is a scalable, convenient and cost-effective solution for multiple business needs, and by digitizing supply chain quality and management, NSF can also help clients improve their ability to proactively address supply chain disruption.
“Papa Johns has partnered with NSF for more than 15 years. Their professionalism and expertise are unmatched. We leverage their technology platform TraQtion™ to house all our international suppliers (900+) and our product specifications (2,000+). It offers our FSQA team a single, searchable database to help drive compliance, risk management and quality standards.”
“Using NSF’s TraQtion™ software, we have been able to save valuable time and resources with an automated process to onboard new suppliers and consolidate our due diligence into one system. Today, we have 98%-99% of our international supply chain mapped and hope to fully close the loop in the next couple of months.”
Transforming the Audit Process
NSF’s Mobile Audit Tool transforms the audit process by seamlessly integrating real-time data syncing to empower auditors in the field. Designed with simplicity and efficiency in mind, the app eradicates the need for cumbersome checklists and guidebooks by providing immediate access to policy notes and scoring guidelines. Its intuitive search functionality allows auditors to swiftly navigate through information, while the signature feature ensures a verifiable conclusion to each audit.
This mobile application not only streamlines the preparation and execution of audits but also enhances the accuracy and reliability of data collection and analysis. By revolutionizing how audits are conducted, NSF’s Mobile Audit Tool app reinforces our commitment to elevating global auditing standards, ensuring that every stakeholder in the food supply chain benefits from unparalleled operational efficiency and compliance adherence.
Cybersecurity
The more technology is embraced in the food, drink and public health industries, the greater the need becomes for organizations to protect themselves from inadvertent or deliberate harm. It’s estimated that $600 billion may be lost to cybercrime annually, based on a report from the Center for Strategic and International Studies. Cybersecurity often isn’t about being threatened by career hackers – a business is just as likely to be compromised by a phishing attack or an employee being tailgated – so continued education and engagement are critical.
NSF’s goal is to make Information Security accessible to all organizations. The NSF CyberSecure platform provides the initial step in a company’s Information Security journey, offering real-time feedback on their existing policies using Artificial Intelligence (AI) technology. Organizations can build their own security framework that encompasses security best practices and customize it to their needs.
NSF CyberSecure Overview
Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification
The Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) program is an important part of the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) overall response to rising cybersecurity threats. It’s a verification mechanism that ensures companies implement proven cybersecurity practices to protect controlled unclassified information. To continue to do business with DoD, would-be suppliers need to be audited and certified by a CMMC Third Party Assessment organization by the end of 2025. NSF was one of the first certification companies to be accredited by DoD to perform this service.
Tony Giles, Director, Information Security, NSF, along with his team, provides assessments for a wide variety of companies that are at different stages of the information security journey.
Tony Giles
Tony Giles
“There are 350,000 suppliers within the Department of Defense supply basin, and I’d say 85% of those are small to mid-sized organizations, many family owned and operated. They’re doing what they can to protect the controlled unclassified information that the government flows down to them, but they need help. And that’s where NSF comes in. We can help them comply with CMMC so they can stay in business and grow.”
Adapting to an Ever-Changing World
7
NSF has consistently demonstrated its unwavering commitment to its core values by staying ahead of the curve.


Adapting to an
Ever-Changing World
NSF has shown its ability to adapt and respond to a rapidly changing world to continue to deliver on its mission. As the world became increasingly interconnected, NSF acknowledged the importance of global standards. Since the 1990s our reach has extended far beyond the United States, with established offices and laboratories around the world; and in turn, this global presence has allowed NSF to harmonize its standards with international counterparts, ensuring products meet global safety and quality standards.
In early 2020, the world was thrust into a global crisis. The COVID-19 pandemic sent shockwaves through communities, economies, and healthcare systems worldwide. It was a crisis of immense magnitude, one that required collective action, resilience, and innovative solutions. NSF had to adapt its own working practices quickly and efficiently, poised to address the monumental challenges the pandemic presented.
NSF was quick to respond, helping team members to work remotely and efficiently, and offering flexibility globally to ensure that NSF team members were supported during this challenging time, and able to continue providing a first-rate service to all their clients in multifaceted and innovative ways. Labs, crucially, had to stay open, and scientists had to be able to access them – so safety measures were put in place to enable NSF’s vital research to continue at a time when the world was shifting its work practices.
Adapting to an Ever-Changing World
In addition, it offered operating advice to its clients about how to function — free introductory COVID-19 training courses to help organizations of any size reduce the likelihood of spread, and looking at long-term changes that could be put in place for companies in the event that such a situation should happen again.
Among the challenges faced, there were several problematic shortages of key medicines, triggered by problems with manufacturing – and that was the case for M&A Pharmachem Ltd, a UK-based manufacturer of pain medication. NSF’s global team of experts rapidly addressed the problem, but it wasn’t a quick fix – it required them to cease manufacturing and provide immediate preventive actions, effectively leaving them unable to place products on the marketplace. NSF’s international team augmented the work of a smaller team who worked onsite at the manufacturing plant. Throughout the two-year process, this expanded and expansive exercise provided a global footprint to the consulting work.
The approach had to be nuanced – NSF worked on the frontline with the manufacturer’s employees to improve procedures, and global experts, trained by NSF (and widely recognized as the best in the industry), were brought in.
As the world recovered from the pandemic, NSF shifted some of its working practices, with hybrid working encouraged and supported. But it also centralized existing offices, providing dynamic, modern and safe work practices as employees begin to spend more time in the office; and the decision was made to make Oxford and Brussels centralized NSF hubs, unifying existing offices and creating headquarters in both countries.
In 2021, NSF reopened its Oxford offices, which had undergone a major refurbishment and rebuild; with a focus on EMEA, the new hub acknowledges in particular NSF’s growing numbers in the UK.
“We have fully remote people, and we have people that work in the office five days a week, and then we have a community of hybrid people that are typically within a 20-to-30-mile radius who come in three days a week. Our Oxford headquarters have undergone a remarkable transformation, resulting in a state-of-the-art workspace for our dedicated team members,” said Michelle Hardy-King, Director, EMEA Retail. “This substantial investment solidifies our unwavering commitment to delivering exceptional services and solutions while fostering a collaborative and inspiring environment for our talented professionals.”
“NSF was instrumental in ensuring our turnaround plan met all the regulator’s concerns. NSF were our trusted advisor during an exceptionally difficult period, providing board-level input on strategy whilst deploying technical experts at sometimes very short notice to cover gaps in competence or expertise internally,”
Climate change, an urgent global concern, has prompted NSF to develop and refine standards that encourage sustainable practices in various industries; for instance, promoting energy-efficient appliances and systems that help mitigate the environmental impact of climate change. As society’s understanding of emerging contaminates deepens, NSF has always established rigorous testing protocols and certifications to ensure the safety and purity of water, food and consumer products. This proactive approach has been instrumental in safeguarding public health and building consumer trust in the face of evolving threats.
With technology rapidly reshaping industry, NSF has proactively integrated AI into its operations and also helped the industry develop new standards and certifications to ensure ethical and responsible use.
NSF’s remarkable journey from its humble beginnings to setting global standards across a wide range of industries is a testament to its adaptability, foresight and commitment to excellence. Whether addressing climate change, emerging contaminants, or the integration of AI, NSF continues to play a pivotal role in shaping industries for a more sustainable and innovative future. Its ability to adapt and respond to these ever-evolving challenges remains crucial for its continued growth and success.
Inspired for Growth
8
NSF’s story has just begun, and we invite you all to be part of its next chapter.


Inspired
for Growth
As I reflect on the first 80 years of NSF, I feel honored to be part of an organization that has played such a crucial role in advancing public health.
Whether it is ensuring the safety of our water systems and food supply chains or enabling the development of life-enhancing products and technologies, NSF continues to have a profound impact on our daily lives.
A lot has happened since NSF was founded in 1944. The world today is much more interconnected, technology has reshaped the way we live and interact with each other, and regulations and consumer values have evolved.
One thing has not changed, and that is NSF’s belief in the power of science and collaboration to advance public health and protect the planet we call home.
NSF’s innovative spirit and adaptability will continue to help the world tackle old challenges such as global epidemics, and address emerging threats such as climate change, cyber-attacks or new contaminants
of concern.
The team at NSF is the key to our success. Without the extraordinary talent of our global team members and their unwavering commitment to our mission, we wouldn’t be who we are today.
At NSF, we are in the business of creating trust, bringing together regulators, manufacturers, and consumers. We are therefore committed to upholding the highest standards of integrity and scientific rigor in everything we do.
As I look forward, I am excited about the opportunity for NSF to fulfill our mission to improve human and planet health on a global scale. But our mission cannot be an isolated endeavor; it is a call to action that extends far beyond our organization.
I’d like to invite you – our friends, clients, partners, and future collaborators – to co-write the next chapter of this book.
Let’s work together for a future with safe and sustainable food, clean water and cutting-edge health products for all.
Pedro Sancha
President & Chief Executive Officer, NSF
Inspired for Growth

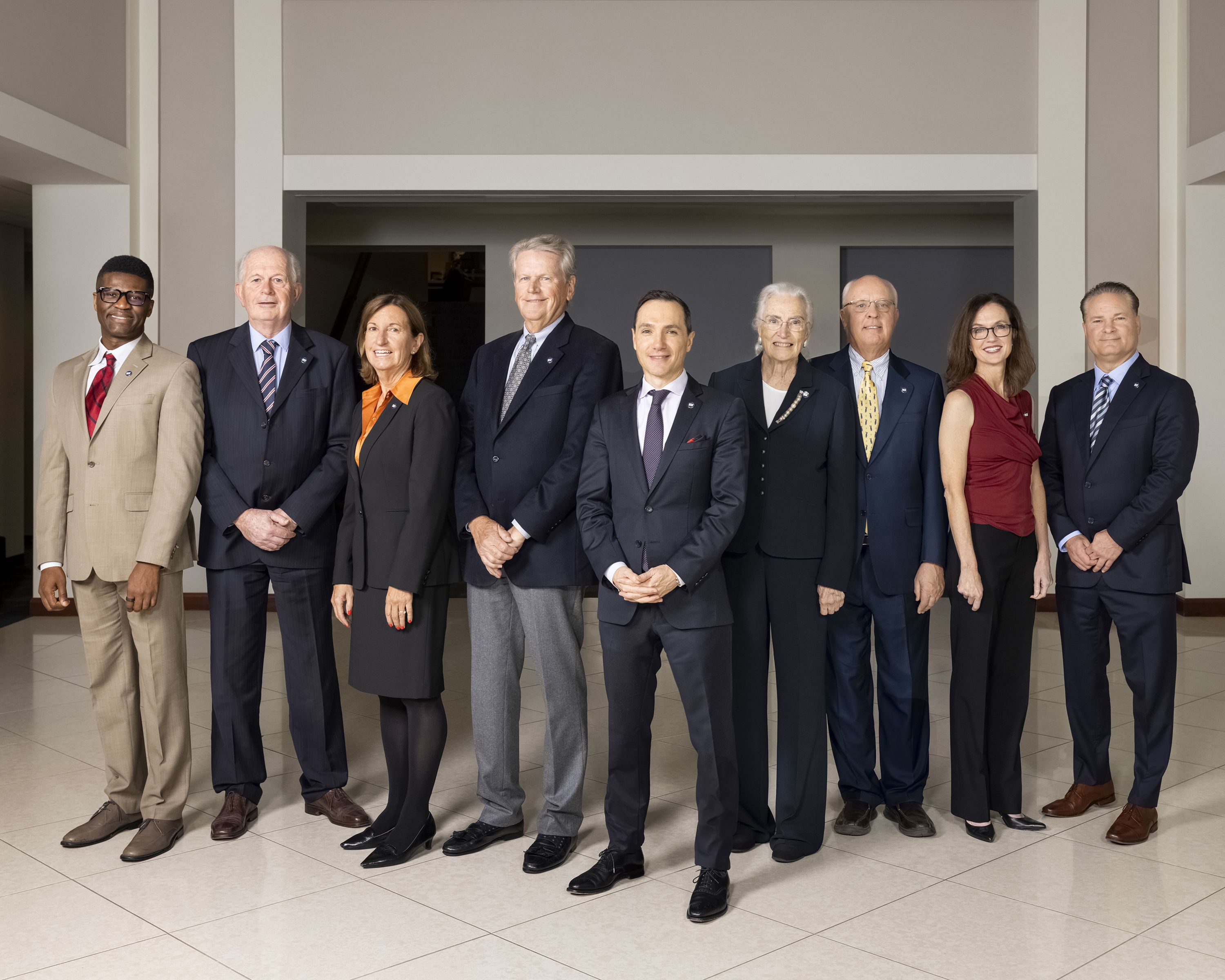
NSF’s Board of Directors From left to right: Ethelbert Williams, Peter Daamen, Joan Menke-Schaenzer, Tom Glasgow, Pedro Sancha, Dr. Mary Jane England, John Graham, Elisabeth Hagen, Todd Gleason. Not pictured: Dean Bergy and Nancy Lurker.
NSF’s Board of Directors From left to right: Ethelbert Williams, Peter Daamen, Joan Menke-Schaenzer, Tom Glasgow, Pedro Sancha, Dr. Mary Jane England, John Graham, Elisabeth Hagen, Todd Gleason. Not pictured: Dean Bergy and Nancy Lurker.
NSF Accreditations
Product Certification Accreditations
(ISO/IEC 17065)
• ANAB (ANSI National Accreditation Board)
• EPA WaterSense®
• EPA ENERGY STAR
• BIFMA
• Sustainable Forestry Initiative Chain of Custody
• Standards Council of Canada Global Retailer and Manufacturer
• Alliance (GRMA)
Inspection Agency Accreditation (ISO/IEC 17020)
• International Accreditation Service
Environmental Certifications
• Silver LEED Certificate
Bottled Water State Certifications
• AZ, CA (includes DWTU program), CT, FL, HI, IN, MD, MI, NC, NV, NJ, NY, PA, SC, VA, VT
Electrical Safety Recognitions
• Accepted in all U.S. states and Canadian provinces & territories
• Additional specific U.S. and Canadian municipality recognition: Albany/Dougherty County, GA; Broward County, FL; Calgary; Chicago; Columbia, MO; Draper, UT; Houston; Los Angeles; Miami; Miami-Dade County, FL; New York, NY; Oklahoma City, OK; Peachtree, GA; Phoenix; Rockville, MD; Salt Lake City; San Jose; Springfield, MO; Tamarac, FL; Vancouver; Winnipeg
Plumbing Recognitions
• Accepted in all U.S. states and Canadian provinces & territories
• Additional specific U.S. municipality recognition: Los Angeles, CA and New York, NY
• Recreational Vehicle Industry Association
• Approved Inspection Agency for DIN CERTCO
Food Safety Accreditations
• Safe Quality Foods (SQF)
• British Retail Consortium (BRC)
• FSSC 22000 ISO 22000
• Best Aquaculture Practices (BAP)
• GLOBALG.A.P.
• CanadaGAP
• PrimusGFS
• International Featured Standards (IFS)
• Red Tractor
QAI (Organics Certification)
• National Organic Program
• Canadian Organic Regime
• Conseil des appellations réservées et des termes valorisants [CARTV] (CAEQ)
• Mexico Organic Products Law
• NSF Standard 305
NSF International Strategic Registrations Accreditations
• ISO/IEC 17021
• IATF 16949
Registered Facility for Testing
• U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration
• U.S. Food and Drug Administration
• U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission
• USDA (Organisms)
• Michigan Liquor Control Commission
• Michigan Department of Environmental Quality
• Michigan Controlled Substance License
• Michigan Department of Community Health
• Connecticut DEA
U.S. Laboratory Accreditations (ISO/IEC 17025) and Recognitions
• Standards Council of Canada
• International Accreditation Service
• National Recognized Testing Lab (OSHA)
• American Society of Sanitary Engineering
Global Laboratory Accreditations (ISO/IEC 17025)
• Brazil (CGRE/Inmetro)
• Peru (INDECOPI)
• United Kingdom (UKAS)
• China (CNAS, Toy Testing, U.S. CPSC)
• Germany (DAkkS)
IACET (International Accreditors
for Continuing Education and Training)
Acknowlegdements
Copywriter: Helen Francis
Design: David Lovelock davidlovelock.com
Copyright NSF 2024
All information correct at time of going to press